Raspberry Pi Pico with 16X2 LCD Display

Hello,
In this article we are going to interface Raspberry Pi Pico with 16X2 LCD Display If you are new to Raspberry Pi Pico and wants to get started then click here.
here you can learn the basics of how to start with raspberry Pi Pico.
Video of raspberry PI Pico & 16×2 LCD
Required Components
List of required components is given below.
Schematic Diagram
Below is the schematic diagram for Raspberry Pi Pico with 16X2 LCD Display
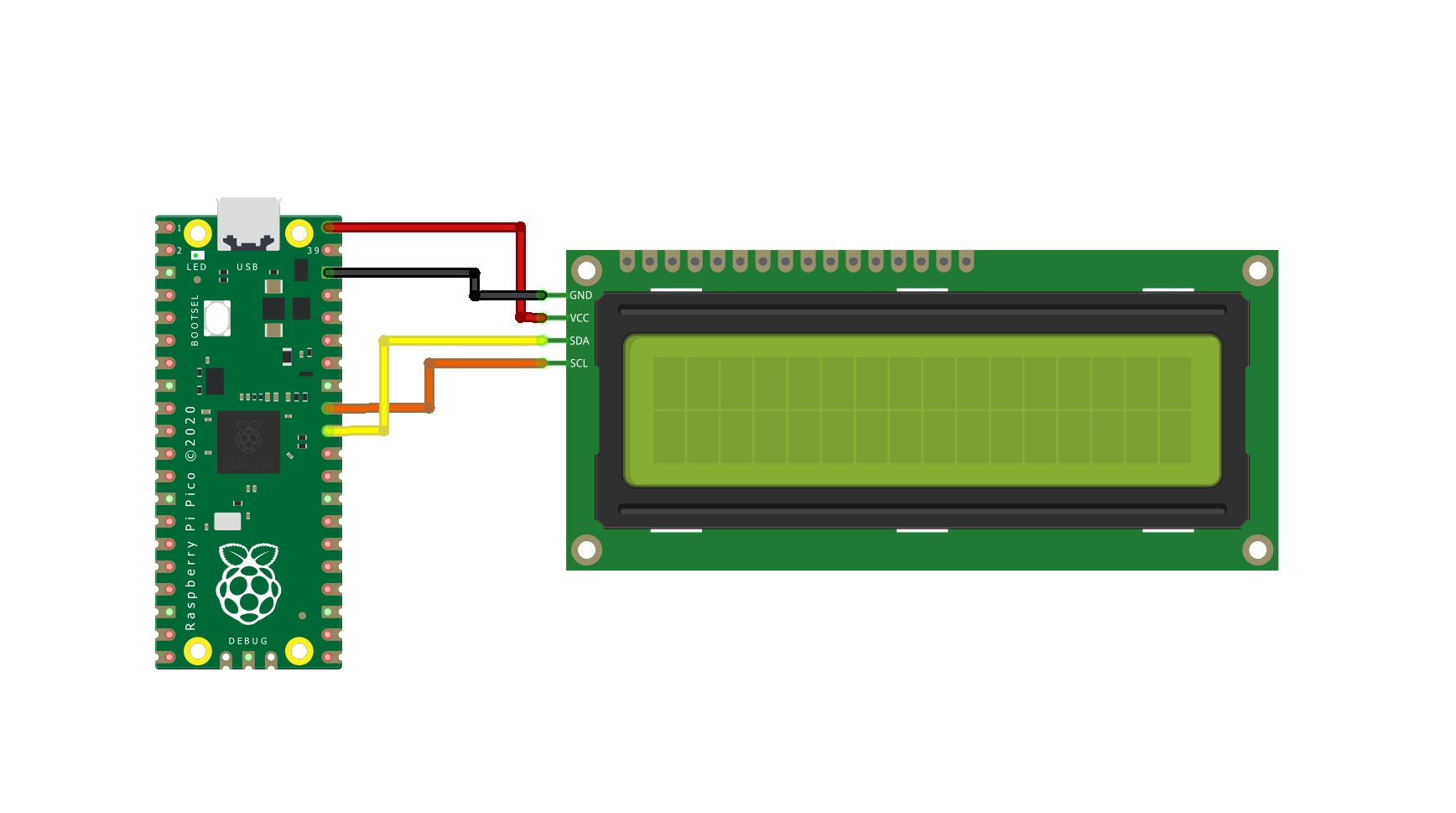
Follow this schematic diagram and make connections.
GND Pin of display with GND Pin of Raspberry Pi Pico
Vcc Pin of display with 5V Pin of Raspberry Pi Pico
SCL Pin of display with GP27 Pin of Raspberry Pi Pico
SDA Pin of OLED display with GP26 Pin of Raspberry Pi Pico
Coding
To write and upload program here i used Thonny IDE. You can download from here.
Here i write code in micropython.
There are three files for code. Two files are library files and another is a main code file.
First make library files.
Copy and paste library code and save in pico as same name as i saved.
Copy paste below code and save in raspberry pi pico as “lcd_api.py”.
import time
class LcdApi:
LCD_CLR = 0x01 # DB0: clear display
LCD_HOME = 0x02 # DB1: return to home position
LCD_ENTRY_MODE = 0x04 # DB2: set entry mode
LCD_ENTRY_INC = 0x02 # --DB1: increment
LCD_ENTRY_SHIFT = 0x01 # --DB0: shift
LCD_ON_CTRL = 0x08 # DB3: turn lcd/cursor on
LCD_ON_DISPLAY = 0x04 # --DB2: turn display on
LCD_ON_CURSOR = 0x02 # --DB1: turn cursor on
LCD_ON_BLINK = 0x01 # --DB0: blinking cursor
LCD_MOVE = 0x10 # DB4: move cursor/display
LCD_MOVE_DISP = 0x08 # --DB3: move display (0-> move cursor)
LCD_MOVE_RIGHT = 0x04 # --DB2: move right (0-> left)
LCD_FUNCTION = 0x20 # DB5: function set
LCD_FUNCTION_8BIT = 0x10 # --DB4: set 8BIT mode (0->4BIT mode)
LCD_FUNCTION_2LINES = 0x08 # --DB3: two lines (0->one line)
LCD_FUNCTION_10DOTS = 0x04 # --DB2: 5x10 font (0->5x7 font)
LCD_FUNCTION_RESET = 0x30 # See "Initializing by Instruction" section
LCD_CGRAM = 0x40 # DB6: set CG RAM address
LCD_DDRAM = 0x80 # DB7: set DD RAM address
LCD_RS_CMD = 0
LCD_RS_DATA = 1
LCD_RW_WRITE = 0
LCD_RW_READ = 1
def __init__(self, num_lines, num_columns):
self.num_lines = num_lines
if self.num_lines > 4:
self.num_lines = 4
self.num_columns = num_columns
if self.num_columns > 40:
self.num_columns = 40
self.cursor_x = 0
self.cursor_y = 0
self.implied_newline = False
self.backlight = True
self.display_off()
self.backlight_on()
self.clear()
self.hal_write_command(self.LCD_ENTRY_MODE | self.LCD_ENTRY_INC)
self.hide_cursor()
self.display_on()
def clear(self):
"""Clears the LCD display and moves the cursor to the top left
corner.
"""
self.hal_write_command(self.LCD_CLR)
self.hal_write_command(self.LCD_HOME)
self.cursor_x = 0
self.cursor_y = 0
def show_cursor(self):
"""Causes the cursor to be made visible."""
self.hal_write_command(self.LCD_ON_CTRL | self.LCD_ON_DISPLAY |
self.LCD_ON_CURSOR)
def hide_cursor(self):
"""Causes the cursor to be hidden."""
self.hal_write_command(self.LCD_ON_CTRL | self.LCD_ON_DISPLAY)
def blink_cursor_on(self):
"""Turns on the cursor, and makes it blink."""
self.hal_write_command(self.LCD_ON_CTRL | self.LCD_ON_DISPLAY |
self.LCD_ON_CURSOR | self.LCD_ON_BLINK)
def blink_cursor_off(self):
"""Turns on the cursor, and makes it no blink (i.e. be solid)."""
self.hal_write_command(self.LCD_ON_CTRL | self.LCD_ON_DISPLAY |
self.LCD_ON_CURSOR)
def display_on(self):
"""Turns on (i.e. unblanks) the LCD."""
self.hal_write_command(self.LCD_ON_CTRL | self.LCD_ON_DISPLAY)
def display_off(self):
"""Turns off (i.e. blanks) the LCD."""
self.hal_write_command(self.LCD_ON_CTRL)
def backlight_on(self):
"""Turns the backlight on.
This isn't really an LCD command, but some modules have backlight
controls, so this allows the hal to pass through the command.
"""
self.backlight = True
self.hal_backlight_on()
def backlight_off(self):
"""Turns the backlight off.
This isn't really an LCD command, but some modules have backlight
controls, so this allows the hal to pass through the command.
"""
self.backlight = False
self.hal_backlight_off()
def move_to(self, cursor_x, cursor_y):
"""Moves the cursor position to the indicated position. The cursor
position is zero based (i.e. cursor_x == 0 indicates first column).
"""
self.cursor_x = cursor_x
self.cursor_y = cursor_y
addr = cursor_x & 0x3f
if cursor_y & 1:
addr += 0x40 # Lines 1 & 3 add 0x40
if cursor_y & 2: # Lines 2 & 3 add number of columns
addr += self.num_columns
self.hal_write_command(self.LCD_DDRAM | addr)
def putchar(self, char):
"""Writes the indicated character to the LCD at the current cursor
position, and advances the cursor by one position.
"""
if char == '\n':
if self.implied_newline:
# self.implied_newline means we advanced due to a wraparound,
# so if we get a newline right after that we ignore it.
pass
else:
self.cursor_x = self.num_columns
else:
self.hal_write_data(ord(char))
self.cursor_x += 1
if self.cursor_x >= self.num_columns:
self.cursor_x = 0
self.cursor_y += 1
self.implied_newline = (char != '\n')
if self.cursor_y >= self.num_lines:
self.cursor_y = 0
self.move_to(self.cursor_x, self.cursor_y)
def putstr(self, string):
"""Write the indicated string to the LCD at the current cursor
position and advances the cursor position appropriately.
"""
for char in string:
self.putchar(char)
def custom_char(self, location, charmap):
"""Write a character to one of the 8 CGRAM locations, available
as chr(0) through chr(7).
"""
location &= 0x7
self.hal_write_command(self.LCD_CGRAM | (location << 3))
self.hal_sleep_us(40)
for i in range(8):
self.hal_write_data(charmap[i])
self.hal_sleep_us(40)
self.move_to(self.cursor_x, self.cursor_y)
def hal_backlight_on(self):
"""Allows the hal layer to turn the backlight on.
If desired, a derived HAL class will implement this function.
"""
pass
def hal_backlight_off(self):
"""Allows the hal layer to turn the backlight off.
If desired, a derived HAL class will implement this function.
"""
pass
def hal_write_command(self, cmd):
"""Write a command to the LCD.
It is expected that a derived HAL class will implement this
function.
"""
raise NotImplementedError
def hal_write_data(self, data):
"""Write data to the LCD.
It is expected that a derived HAL class will implement this
function.
"""
raise NotImplementedError
def hal_sleep_us(self, usecs):
"""Sleep for some time (given in microseconds)."""
time.sleep_us(usecs) Now copy paste below code and save it as “pico_i2c_lcd.py”.
from lcd_api import LcdApi
from machine import I2C
from time import sleep_ms
DEFAULT_I2C_ADDR = 0x27
# Defines shifts or masks for the various LCD line attached to the PCF8574
MASK_RS = 0x01
MASK_RW = 0x02
MASK_E = 0x04
SHIFT_BACKLIGHT = 3
SHIFT_DATA = 4
class I2cLcd(LcdApi):
"""Implements a character based lcd connected via PCF8574 on i2c."""
def __init__(self, i2c, i2c_addr, num_lines, num_columns):
self.i2c = i2c
self.i2c_addr = i2c_addr
self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytearray([0]))
sleep_ms(20) # Allow LCD time to powerup
# Send reset 3 times
self.hal_write_init_nibble(self.LCD_FUNCTION_RESET)
sleep_ms(5) # need to delay at least 4.1 msec
self.hal_write_init_nibble(self.LCD_FUNCTION_RESET)
sleep_ms(1)
self.hal_write_init_nibble(self.LCD_FUNCTION_RESET)
sleep_ms(1)
# Put LCD into 4 bit mode
self.hal_write_init_nibble(self.LCD_FUNCTION)
sleep_ms(1)
LcdApi.__init__(self, num_lines, num_columns)
cmd = self.LCD_FUNCTION
if num_lines > 1:
cmd |= self.LCD_FUNCTION_2LINES
self.hal_write_command(cmd)
def hal_write_init_nibble(self, nibble):
"""Writes an initialization nibble to the LCD.
This particular function is only used during intiialization.
"""
byte = ((nibble >> 4) & 0x0f) << SHIFT_DATA
self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytearray([byte | MASK_E]))
self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytearray([byte]))
def hal_backlight_on(self):
"""Allows the hal layer to turn the backlight on."""
self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytearray([1 << SHIFT_BACKLIGHT]))
def hal_backlight_off(self):
"""Allows the hal layer to turn the backlight off."""
self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytearray([0]))
def hal_write_command(self, cmd):
"""Writes a command to the LCD.
Data is latched on the falling edge of E.
"""
byte = ((self.backlight << SHIFT_BACKLIGHT) | (((cmd >> 4) & 0x0f) << SHIFT_DATA))
self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytearray([byte | MASK_E]))
self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytearray([byte]))
byte = ((self.backlight << SHIFT_BACKLIGHT) | ((cmd & 0x0f) << SHIFT_DATA))
self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytearray([byte | MASK_E]))
self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytearray([byte]))
if cmd <= 3:
# The home and clear commands require a worst case delay of 4.1 msec
sleep_ms(5)
def hal_write_data(self, data):
"""Write data to the LCD."""
byte = (MASK_RS | (self.backlight << SHIFT_BACKLIGHT) | (((data >> 4) & 0x0f) << SHIFT_DATA))
self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytearray([byte | MASK_E]))
self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytearray([byte]))
byte = (MASK_RS | (self.backlight << SHIFT_BACKLIGHT) | ((data & 0x0f) << SHIFT_DATA))
self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytearray([byte | MASK_E]))
self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytearray([byte]))Now, main code is given as below.
from pico_i2c_lcd import I2cLcd
from machine import I2C
from machine import Pin
i2c = I2C(id=1,scl=Pin(27),sda=Pin(26),freq=100000)
lcd = I2cLcd(i2c, 0x27, 2, 16) # LCD 16x2
lcd.putstr('Hello World')from pico_i2c_lcd import I2cLcd
from machine import I2C
from machine import Pin
i2c = I2C(id=1,scl=Pin(27),sda=Pin(26),freq=100000)
lcd = I2cLcd(i2c, 0x27, 2, 16) # LCD 16x2
lcd.putstr('Hello World')Save above code in Raspberry Pi Pico as “main.py” and run the code. It will print “Hello World” on display.